What is a Core Mobile Network?
What a Core Mobile Network is can best be described as the following. The Core Network is the heart of telecommunications, responsible for routing voice, data, and multimedia traffic across vast networks, ensuring seamless connectivity and efficient communication.
It plays a pivotal role in ensuring seamless connectivity, efficient communication, and the integration of various services. In this comprehensive exploration, we will dissect the Core Network into its four primary components, shedding light on their intricacies and significance.
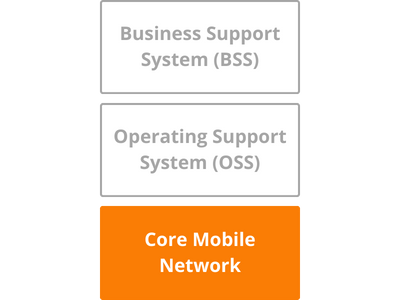
From a Mobile Brand / MVNO point of view the Core Mobile Network is at the bottom, below the Business Support System (BSS) and the Operating Support System (OSS).
Most of the types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs make use of the Core Mobile Network elements of the MNO or MVNE (depending of on the setup). For more details about this see: Different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs.
What do you need to know about the Core Network?
Core Mobile Network Switching
Switching is the foundational component of the Core Mobile Network, responsible for routing and relaying communication between different network nodes.
It determines how voice and data packets are directed within the network, ensuring that messages reach their intended destinations.
What are the key functions of Switching within the Core Mobile Network?
Call Routing
Switching systems routing incoming and outgoing voice calls to the appropriate appropriate destination, whether it’s another phone on the same network or an external network.
Data Packet Routing
For data communication, switching decides the path data packets should take to reach their destination. This involves decisions at both the network and transport layers.
Protocol Conversion
Switches can perform protocol conversion, allowing communication between networks that use different communication standards.
Load Balancing
In high-traffic scenarios, switching systems distribute communication load across multiple routes to prevent congestion and ensure efficient data transfer.
What is the importance of Switching within the Core Network?
Switching is the backbone of communication within a telecommunications network. It ensures that messages, whether voice or data, are directed to the correct destination efficiently. Efficient switching minimizes delays and enhances overall network performance.
Integration with Other Core Network Components
Switching interacts closely with Routing to determine the optimal path for data transmission. It also interfaces with Security to enforce security protocols and protect communication channels.
Core Mobile Network Routing
Routing in the Core Mobile Network is responsible for directing data packets to their destinations across complex telecommunications networks.
It involves determining the best path for data transmission based on factors such as network topology, traffic load, and latency considerations.
What are the key functions of Routing within the Core Network?
Path Determination
Routing algorithms calculate the most efficient path for data packets to traverse from source to destination, considering network conditions.
Dynamic Routing
Routing systems adapt to changing network conditions by dynamically selecting routes that optimize data transmission.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Routing considers QoS requirements, ensuring that high-priority traffic receives preferential treatment to meet service level agreements (SLAs).
Network Redundancy
Routing mechanisms often incorporate redundancy to provide backup paths in case of network failures, improving network resilience.
What is the importance of Routing within the Core Network?
Routing is critical for ensuring data packets reach their intended destinations efficiently and reliably. It plays a key role in minimizing latency, optimizing network utilization, and ensuring consistent network performance.
Integration with other Core Network Components:
Routing closely interacts with Switching to determine the best paths for communication. It collaborates with Security to ensure secure data transmission, especially over public networks.
Core Mobile Network Security
Security within the Core Mobile Network is paramount to safeguard data, communication channels, and network infrastructure.
It encompasses a range of measures and protocols designed to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats.
What are the key functions of Security within the Core Network?
Access Control
Security measures restrict access to network resources, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can connect to the network.
Data Encryption
Encryption techniques are employed to secure data in transit, making it unreadable to unauthorized entities.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention
Security systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and take action to prevent potential threats.
Authentication and Authorization
Users and devices are authenticated before they are granted access to network resources. Authorization policies define what actions authorized entities can perform.
Firewall Protection
Firewalls are deployed to filter incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking potentially harmful data packets.
What is the importance of Security within the Core Network?
Security is fundamental for protecting sensitive data, maintaining network integrity, and ensuring the confidentiality and availability of communication channels. Robust security measures are essential to safeguard against cyberattacks and data breaches.
Integration with Other Core Network Components
Security collaborates with Switching and Routing to enforce security policies and protocols throughout the network. It also interfaces with Monitoring to detect and respond to security incidents.
Core Network Monitoring
Monitoring within the Core Mobile Network involves the continuous surveillance of network performance, traffic patterns, and security threats.
It provides real-time insights into network health and helps identify and address issues promptly.
What are the key functions of Monitoring within the Core Network?
Performance Monitoring
Monitoring systems track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as latency, bandwidth utilization, and packet loss to ensure optimal network performance.
Traffic Analysis
These systems analyze network traffic patterns to identify anomalies, congestion points, and potential security threats.
Alerting and Reporting
Monitoring systems generate alerts and reports to inform network administrators of issues, allowing for quick resolution.
Capacity Planning
Data from monitoring helps in capacity planning, enabling network expansion or optimization based on observed usage patterns.
What is the importance of Monitoring within the Core Network?
Monitoring is essential for maintaining network reliability and performance. It enables proactive issue identification and resolution, ensuring that the network meets operational and service quality expectations.
Integration with Other Core Network Components:
Monitoring collaborates with all other Core Network components to provide real-time insights into network performance, security threats, and traffic patterns. It interfaces with Security to detect and respond to security incidents promptly.
Core Network Summary
The Core Network serves as the central hub of telecommunications, orchestrating the flow of voice, data, and multimedia traffic while integrating various network elements and service elements. Network elements such as SMS-C, GGSN, PGW, PCRF, DPI, IMS, MSC, HSS, USSD, SBC, SCP, HLR, MGW, etc. and service elements like Prepaid or Postpaid voice, SMS, and data, Postpaid real-time rating, Web shop, and Web portal play integral roles within this intricate ecosystem, facilitating secure, efficient, and monetizable communication.
With a robust Core Network and its network and service elements, telecommunications providers can uphold the quality of their services, safeguard data, and meet the connectivity and billing needs of their customers in a rapidly changing digital world.






